New Sanctions Group Paper: Four Key Steps to Constrain Russia in 2024 and Beyond
 The Yermak-McFaul International Working Group on Russian Sanctions has published Working Group Paper #18: “Energy Sanctions: Four Key Steps to Constrain Russia in 2024 and Beyond”. The analysis highlights the urgent need for strengthened energy sanctions to constrain Russia’s military aggression against Ukraine, as the full-scale war approaches its second anniversary.
The Yermak-McFaul International Working Group on Russian Sanctions has published Working Group Paper #18: “Energy Sanctions: Four Key Steps to Constrain Russia in 2024 and Beyond”. The analysis highlights the urgent need for strengthened energy sanctions to constrain Russia’s military aggression against Ukraine, as the full-scale war approaches its second anniversary.
The study reveals Russia’s significant vulnerability due to its reliance on oil and gas exports for foreign exchange and government revenues. The EU embargo and G7 price caps on Russian oil have deprived Russia of approximately $113 billion in export revenues since the start of the full-scale invasion, with an additional estimated loss of $55 billion in gas export revenues due to Europe’s diversification away from Russian gas.
The sanctions have already led to a 29% reduction in total exports, a 63% reduction in the trade surplus, and a 79% reduction in the overall current account balance in 2023 vs. 2022, placing a significant strain on Russia’s macroeconomic stability.
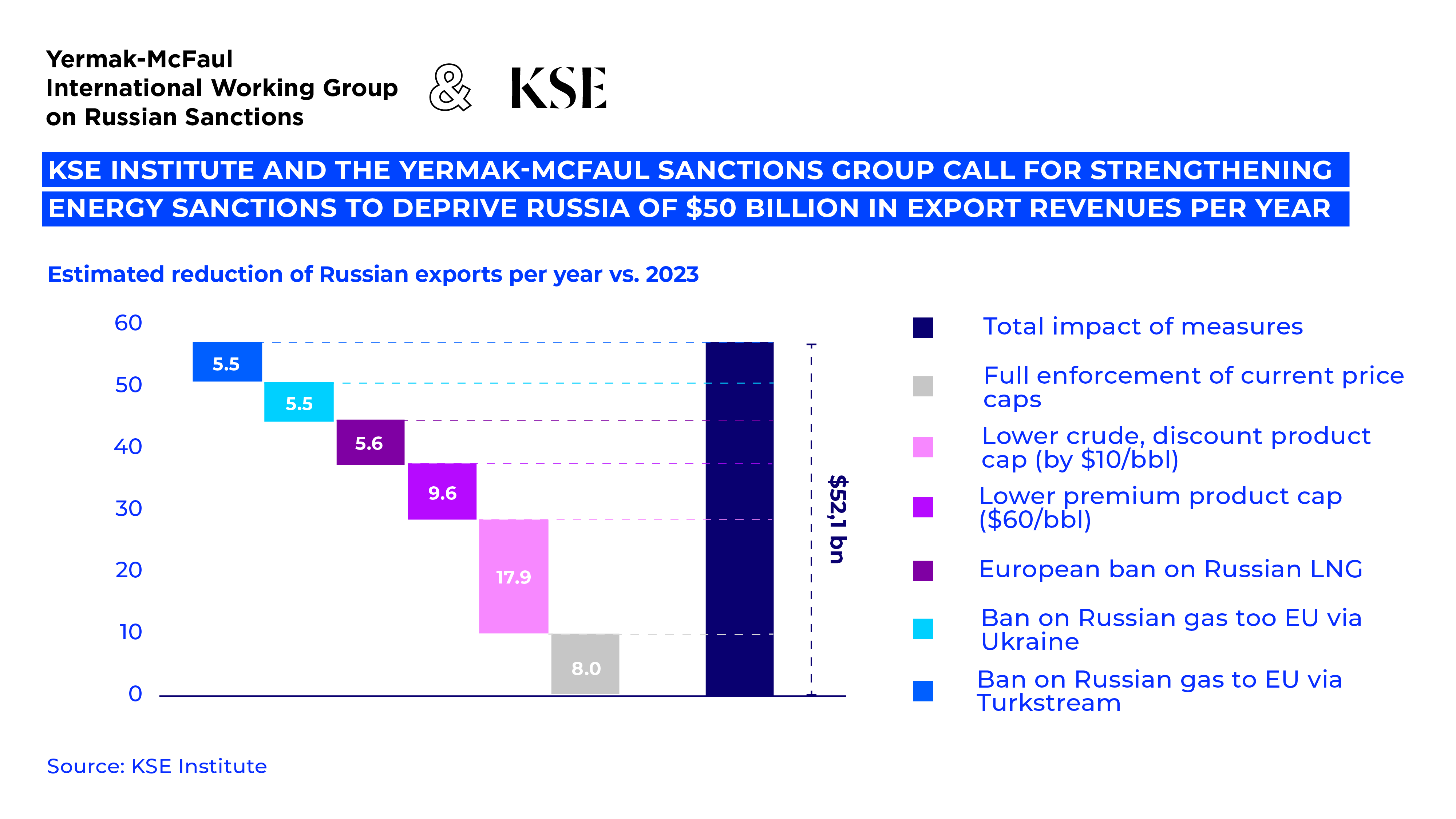
The Working Group calls for immediate action to further squeeze Russia’s ability to finance its war on Ukraine. The paper makes four key recommendations to put pressure on Russia’s economy and undermine its war effort.
Key recommendations:
• Stop the Russian Shadow Fleet: Tighten sanctions on shadow tankers and enforce oil spill insurance requirements to force Russia to use the mainstream fleet that complies with price cap regulations. Strengthen investigations and penalties to increase the costs and risks for those who evade sanctions.
• Lower Price Caps: After ensuring the price caps’ effectiveness and leverage by addressing the shadow fleet challenge and stepping up enforcement, reduce the caps on crude oil and refined products. In a first step, the caps for crude and discounted products should be lowered by $10/bbl and the one for premium products by $40/bbl. This would reduce Russia’s foreign exchange inflows by $25-30 billion annually.
• Complete the EU and G7 Ban on Russian Hydrocarbons: Implement a full ban on Russian LNG and pipeline gas to Europe, demonstrating a commitment to cutting off significant future export revenues for Russia and encouraging energy diversification.
• Isolate Russia’s Oil and Gas Sector: Restrict the Russian oil and gas sector’s access to critical Western technology and services. With restrictions in place since 2014 and further exits of foreign companies after February 2022 already impacting the industry, a full cut-off would hamper LNG production and increase oil production costs.
The proposed measures are estimated to reduce Russia’s export revenues by more than $50 billion annually, significantly reducing its foreign exchange inflows. This strategy aims to critically weaken Russia’s economic support for its military efforts.
The full text of the paper “Energy Sanctions: Four Key Steps to Constrain Russia in 2024 and Beyond” by the experts of the International Working Group on Russian Sanctions is available via link.
Contacts


